How to ingest Web Content in Fewlogs
Ingesting website content into your Fewlogs libraries is a great way to add high-quality material to enhance your AI content generation. Follow these steps to easily ingest entire websites or specific pages into your account.
First, identify a website that contains content relevant to your niche. For example, if you run a sailing blog, you may want to ingest articles about knots and sailing techniques.
Next, grab the home page URL of the site or a specific category page you want to ingest. This will act as the starting point for the crawler.
For example, to ingest all content related to a particular category from domain.com, your starting URL could be https://domain.com/knots, which will discover links recursively from that category page and ingest any page under it.
Using a category page URL scopes the ingestion, while the home page URL will ingest the entire site.
For more advanced use cases, you can use a prefix to limit your ingestion.
The prefix allows you to limit what pages are ingested. You can set the prefix in the “Only ingest URLs starting with” text field, and if it’s left empty, it will use the URL field as the prefix to match.
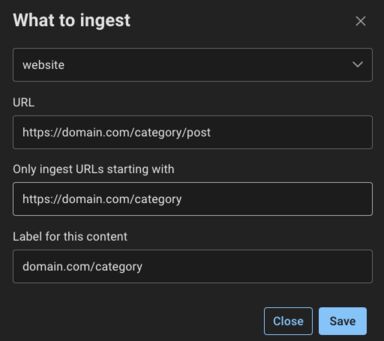
By removing the slug /post, the crawler will crawl any post within the category /category, thus broadening the scope compared to the initial URL. This is particularly helpful when the website lacks a category page.
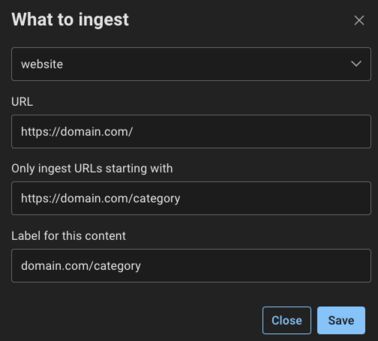
You can give a more generic URL to start the crawl but limit the ingestion to a particular prefix. Doing this will discard any content coming from pages that don’t start with the /category slug.
- Use category pages or targeted sections of sites whenever possible, rather than ingesting everything. This will keep your content ingestion cost-effective.
- Periodically re-ingest sites to get fresh content as it's published.
- Ingest from authoritative, high-quality sites in your niche. Avoid low-quality content as it may introduce false facts in your library.
- Ingesting websites is a one-off, it won’t ingest any new or updated content that is published after the initial ingestion is finished. You can re-ingest the source but keep in mind that it needs to re-crawl everything again, thus consuming similar credits. While we work on enhancing the identification of new or updated pages, we advise you to keep your sources granular and re-ingest only what you need, with wide periodic intervals such as monthly.